G I Surgery
Gastrointestinal surgery is a treatment for medical conditions involving the digestive system. This involves the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.

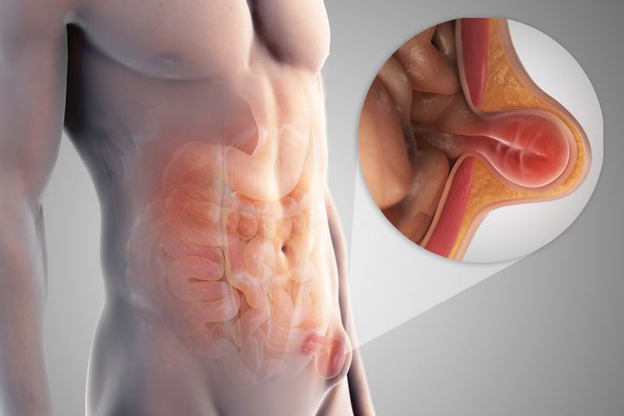
Hernia Surgery
A hernia occurs when an internal organ or body part swells up through the muscle or tissue that usually maintains it in place, causing a protrusion beneath the skin. The majority of hernias occur in the abdominal area. Hernia surgery is the surgical procedure performed to treat hernias.
Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery, also known as metabolic surgery or weight loss surgery, is widely recognized as one of the most effective means of assisting and maintaining weight reduction. It has the potential to reduce future health problems, enhance the quality of life, and improve life expectancy.
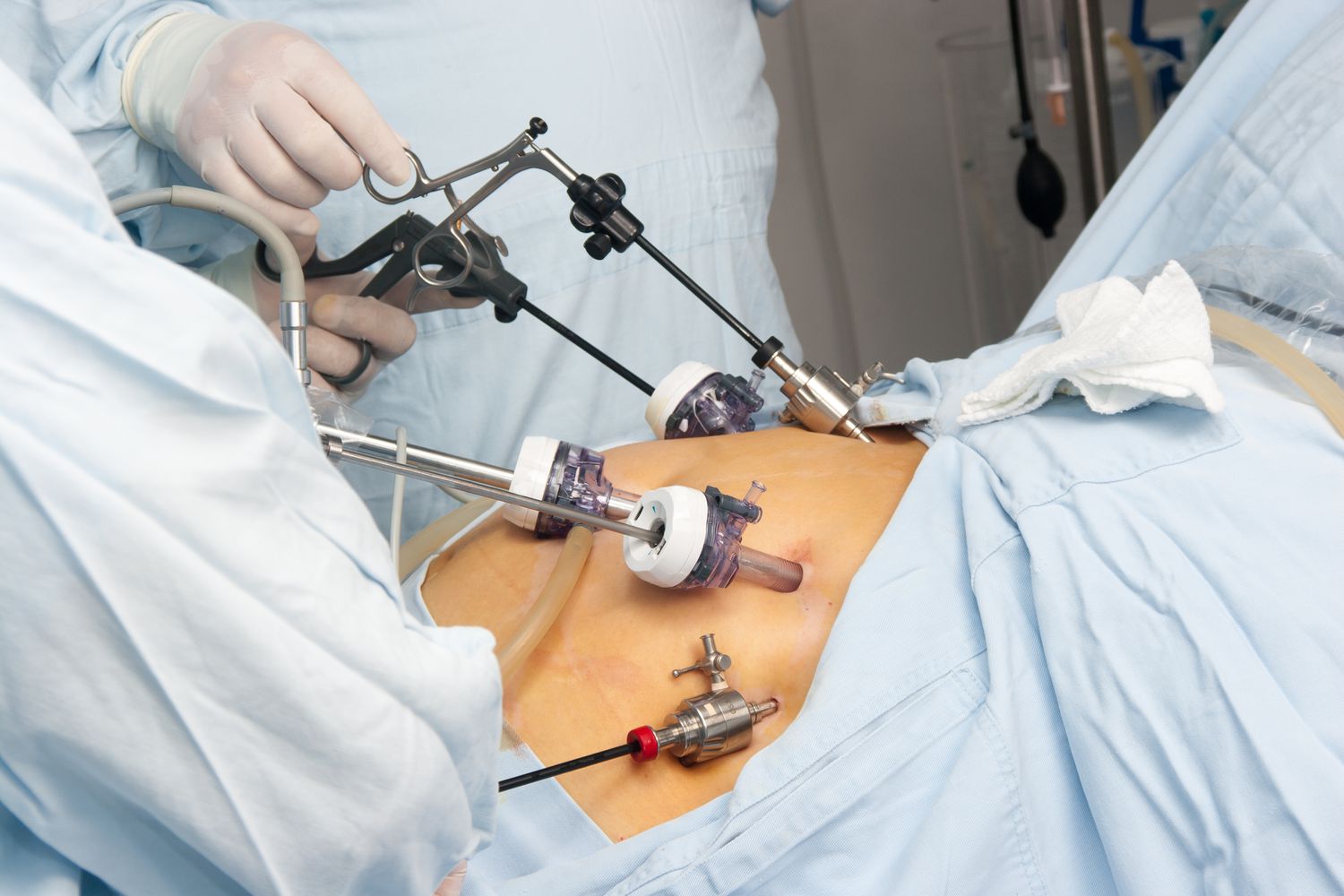
G I Cancer Surgery
GI cancer surgery is the medical procedure used to treat gastrointestinal cancer. Medical treatment for GI cancer varies depending on the kind of cancer. Some therapies are designed to destroy cancer cells; others are designed to prevent cancer cells from growing, treat their abnormalities, or reduce the likelihood of them returning.
24hrs I C U facility
The intensive care unit, or ICU, is the department that treats and manages patients who have serious or life-threatening conditions or injuries. Patients who have been in traumatic accidents, are dealing with post-surgical problems, or have severe and difficult-to-treat infections may require admission to the ICU.
Clinical Gastroenterology
Clinical Gastroenterology is a series of concise monographs on diseases commonly encountered in the clinical practice of Internal Medicine and Gastroenterology. Particular emphasis is placed on areas in which knowledge is advancing rapidly. Each volume is concise, concentrating on "clinical pearls," and new advances in diagnostic and therapeutic technology. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology (CGH) publishes clinical articles on all aspects of the digestive system, including the liver and pancreas.
Diagnostic & Therapeutic Upper G I Scopy
An upper GI endoscopy or EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) is a procedure to diagnose and treat problems in your upper GI (gastrointestinal) tract. The upper GI tract includes your food pipe, stomach, and the first part of your small intestine.
Being sedated during the procedure will put you into a moderate to deep sleep, so you will not feel any discomfort when the endoscope is inserted through the mouth and into the stomach. Moreover, most people undergoing sedation will have some short-term memory loss, so you will not recall the examination itself.
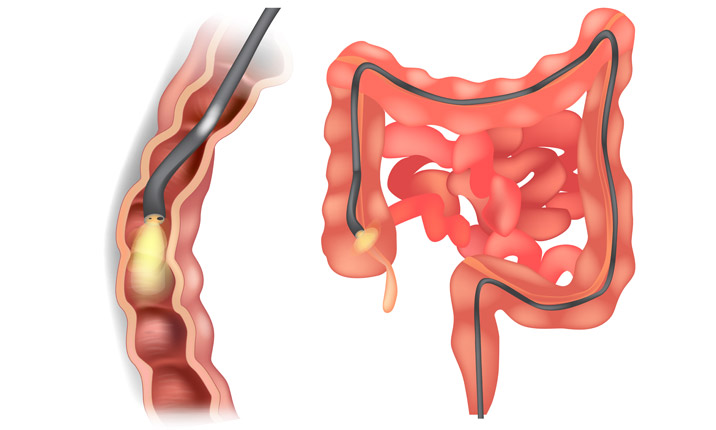
Diagnostic & Therapeutic Lower G I Scopy
The endoscopy procedure. An endoscopy isn't usually painful, and most people only experience some mild discomfort, similar to indigestion or a sore throat. The procedure is usually carried out while you're conscious. You may be given a local anesthetic to numb a specific area of your body.
Endoscopy is a procedure that allows a doctor to view the inside of a person's body. Originally, endoscopy was only used in the esophagus, stomach, and colon. Now, doctors use endoscopy to diagnose diseases of the ear, nose, throat, heart, urinary tract, joints, and abdomen.
Endoscopic Ultrasonography
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a minimally invasive procedure to assess digestive (gastrointestinal) and lung diseases. A special endoscope uses high-frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the lining and walls of your digestive tract and chest, nearby organs such as the pancreas and liver, and lymph nodes.
When combined with a procedure called fine-needle aspiration, EUS allows your doctor to sample (biopsy) fluid and tissue from your abdomen or chest for analysis. EUS with fine-needle aspiration can be a minimally invasive alternative to exploratory surgery.
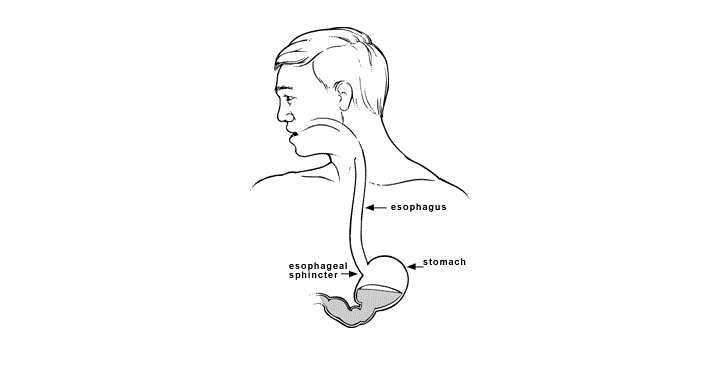
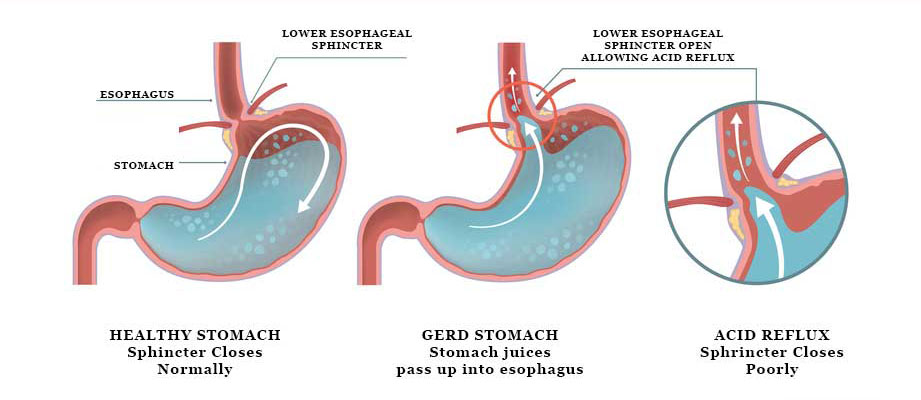
Manometry
Esophageal manometry is a test used to measure the function of the lower esophageal sphincter (the valve that prevents reflux of gastric acid into the esophagus) and the muscles of the esophagus (see diagram). This test will tell your doctor if your esophagus is able to move food to your stomach normally. Knowing why you might be experiencing a problem with your digestive system, helps to understand the swallowing and digestive processes.
Dietary Consultation
Dietary consultations at BMI Healthcare are designed to evaluate the patient's eating habits and food consumption and provide advice where necessary.
The clinical or consultant dietician will review the patient’s medical charts and talk with patients' families. They will work with other health care professionals, such as gastroenterologists and oncologists to provide nourishment, nutritional programs, and instructional presentations to benefit people of all ages, and with a variety of health conditions.


Obesity Management
Management of obesity can include lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery. The main treatment for obesity consists of dieting and physical exercise. The most effective treatment for obesity is bariatric surgery. Surgery for severe obesity is associated with long-term weight loss and decreased overall mortality.
To boost your activity level: Exercise. People who are overweight or obese need to get at least 150 minutes a week of moderate-intensity physical activity to prevent further weight gain or to maintain the loss of a modest amount of weight.
pH and Impedance
Esophageal impedance-pH monitoring provides quantitative data on esophageal acid exposure and has the ability to correlate the symptoms with acid exposure events. The nomenclature for the reflux patterns detected in impedance-pH monitoring as well as the normal values have been determined. Combined esophageal pH-impedance monitoring allows detection of nearly all gastroesophageal reflux episodes, acid as well as nonacid. However, the role of nonacid reflux in the pathogenesis of symptoms is poorly known. The aim of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic yield of this technique in patients with suspected reflux symptoms while on or off PPI therapy.


Day Care Ward
The Gastrohub Hospital has daycare wards for both general and private patients. Patients are admitted for a few hours and treated which otherwise would have been required.
We provide daycare services for all kinds of surgeries, chemotherapy, endoscopy, preventive health programs, and even certain types of outpatient antibiotic therapy. Our dedicated surgical daycare suite allows patients quick and efficient single-point admission.
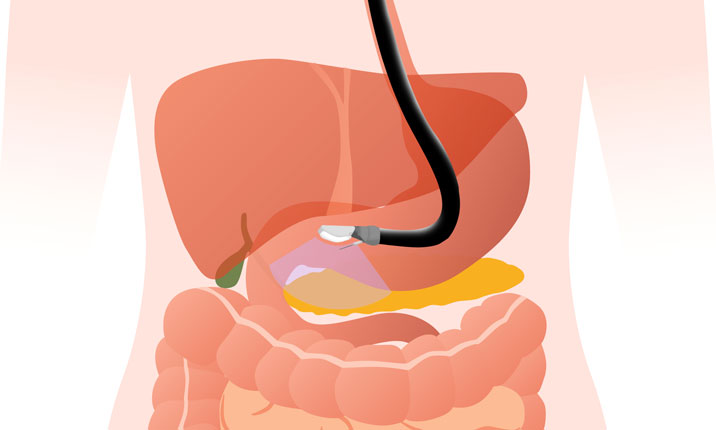
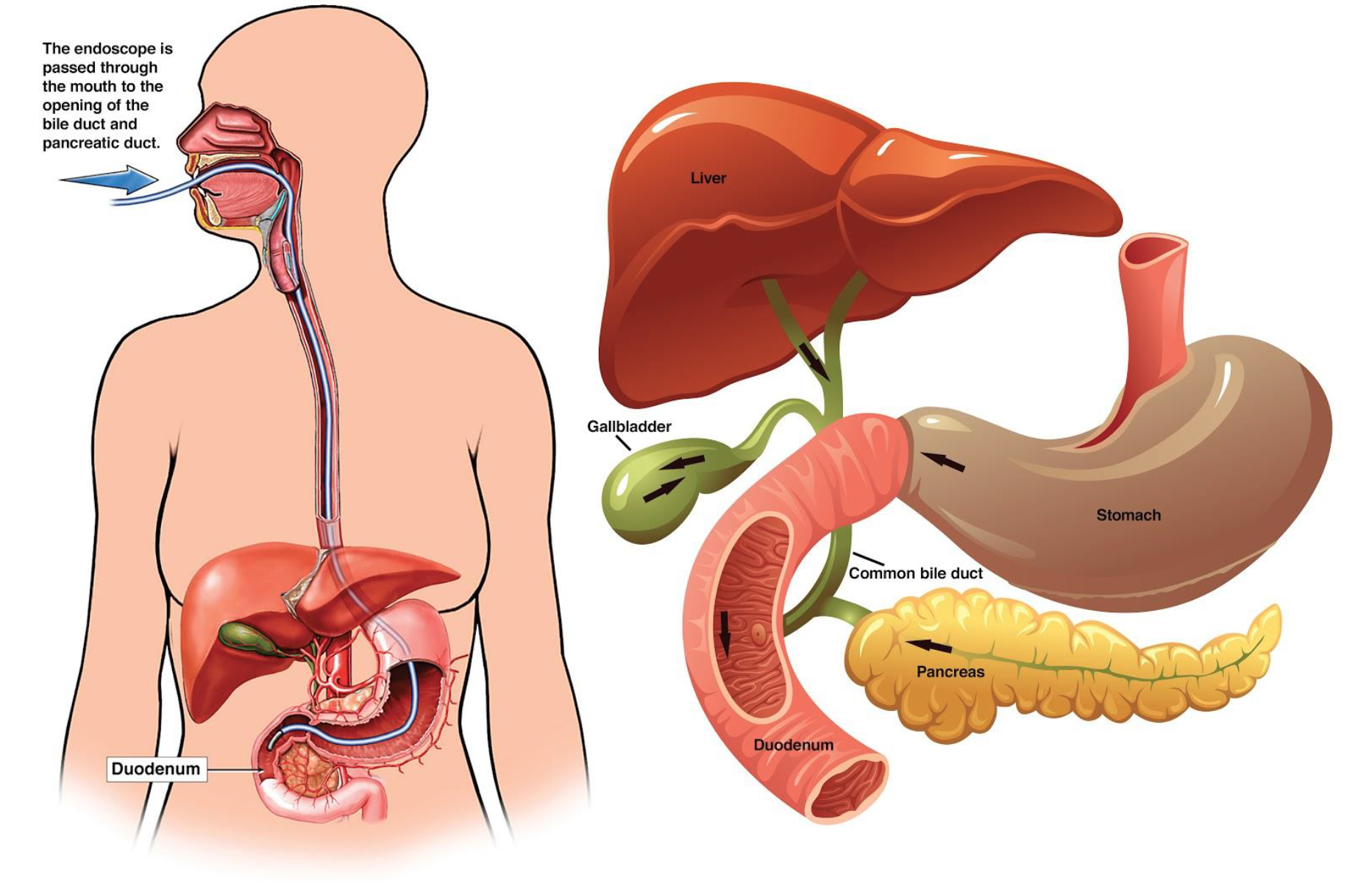
ERCP
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography is a technique that combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat certain problems of the biliary or pancreatic ductal systems.
ERCP is a procedure that enables your physician to examine the pancreatic and bile ducts. A bendable, lighted tube (endoscope) about the thickness of your index finger is placed through your mouth and into your stomach and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum).
Special Liver Clinic
Will offer a comprehensive assessment, counseling, and therapy for patients with fatty liver. Special packages will be available and patients can seek advice from a liver specialist, or dietician and will also be counseled on lifestyle changes, exercise, weight loss, etc.
Your clinic's experts in hepatology, radiology, pathology, liver surgery, and other specialties collaborate closely to tailor a care plan to your specific needs.
Special IBC Clinic
Treatment for inflammatory breast cancer usually starts with chemotherapy. Chemotherapy before surgery is called neoadjuvant or preoperative therapy. After chemotherapy, people with inflammatory breast cancer usually have surgery followed by radiation therapy to the breast or chest wall. Early IBC symptoms may include persistent itching and the appearance of a rash or small irritation similar to an insect bite. The breast typically becomes red, swollen, and warm. The skin may appear pitted like an orange peel, and nipple changes such as inversion, and flattening.


